Generator of Root ANAtomy in R [GRANAR]
![Generator of Root ANAtomy in R [GRANAR]](/images/granar1.jpg)
GRANAR is a computational tool that simulates root anatomical networks. GRANAR begins with a detailed cross-sectional image of the root, capturing its intricate anatomical features and transform the image into a digital root anatomical network, showcasing the cellular intricacies and connections. GRANAR offers a detailed representation of root network structure, pinpointing the location of each cell and tissue. Let’s delve deeper into how GRANAR constructs the root structure and the parameters it uses:
- 🌾 GRANAR begins by extracting key anatomical traits from root cross-section images, offering a detailed insight into the root’s anatomy.
- 🌍 Using the extracted anatomical traits measured along the root axes, linear regressions are computed against the distance to the root tip for each root type. This helps understand the variations in anatomical traits along the root.
- 🌦️ The coefficients derived from the linear models help estimate GRANAR’s input parameters at every desired location along the root. If no significant difference is observed between the distance along the root and the anatomical traits from a uniform model, the average value of the anatomical traits is utilized.
- 💧 For the relationship between the size of the stele and the metaxylem, a Napierian logarithmic transformation is applied to both the stele area and the metaxylem. This relationship is then integrated into the GRANAR parametrization procedure.
- 🚜 With the input parameters defined, GRANAR can simulate representative root cross-sections for each root type at any longitudinal position.
- 🌾 Besides the root cross-sections, locations of hydrophobic barriers and metaxylem maturation zones are added based on staining signals, offering more details about the root’s anatomy, especially concerning water movement barriers.
Parameters Used by GRANAR
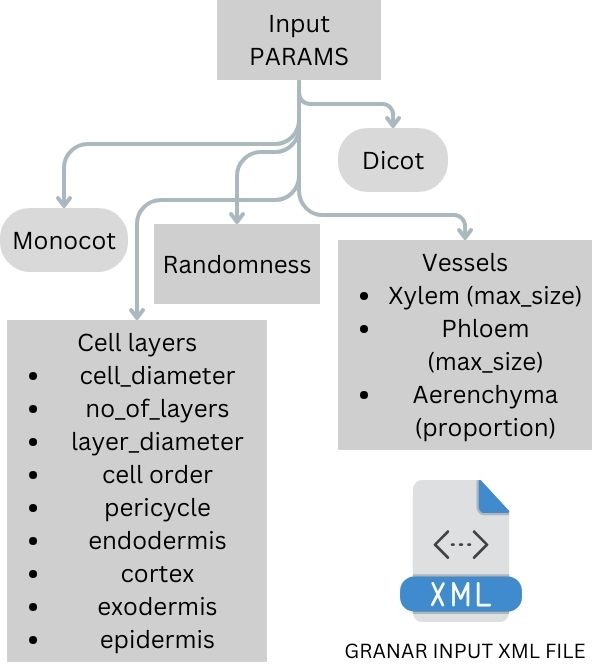
GRANAR uses various anatomical parameters to simulate the cellular anatomy of roots. Each parameter represents a specific aspect of the root’s structure. For instance, ‘parenchyma’ refers to the primary tissue in plants, involved in storage, photosynthesis, and secretion. ‘Pericycle’ is a layer of cells surrounding the vascular bundles in plants, playing a crucial role in secondary growth. ‘Cortex’ is the tissue occurring between the epidermis and the vascular tissue, responsible for storage in roots. ‘Xylem’ is the vascular tissue responsible for the transport of water and nutrients from the roots to the shoots and leaves. Let’s delve deeper into the specific parameters GRANAR uses:
- 🌾 Stelar parenchyma: This refers to the parenchyma cells found within the stele. Parameters include Cell diameter and Diameter of the stele tissue (excluding pericycle).
- 🌍 Pericycle: A layer of cells that can give rise to lateral roots. Parameters include Cell diameter and Number of layers.
- 🌦️ Endodermis: The innermost layer of the cortex, playing a role in regulating the transfer of substances from the soil to the vascular system. Parameters include Cell diameter and Number of layers.
- 💧 Cortex: The primary tissue between the epidermis and the vascular bundles. Parameters include Cell diameter and Number of layers.
- 🚜 Exodermis: The outermost layer of cells in the root, aiding in preventing water loss. Parameters include Cell diameter and Number of layers.
- 🌾 Epidermis: The outermost layer of cells covering the root. Parameters include Cell diameter and Number of layers.
- 🌍 Xylem: Responsible for transporting water and nutrients. Parameters include Max cell diameter, Number of xylem poles, and Ratio (protoxylem vs metaxylem).
- 🌦️ Aerenchyma: Air-filled cavities within the plant tissue, aiding in gas exchange. Parameters include Proportion and Number of radial cavities.
GRANAR Features
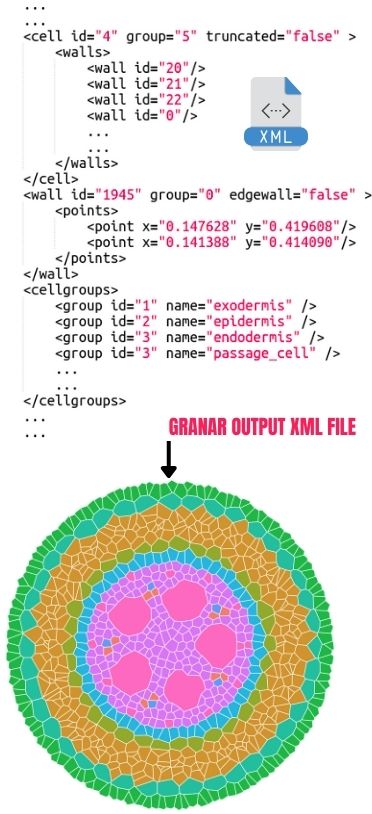
GRANAR is a versatile tool designed for simulating and analyzing root anatomy. Here’s a glimpse of its key capabilities:
deldir alphahull retistruct
🌳 Seamless Integration: Features a MECHA-GRANAR connection for smooth data exchange in XML format, essential for radial conductivity calculations.
💧 ImageJ Compatibility: Integrates with ImageJ software for extracting anatomical features from specific datasets.
🌞 Open Data: Advocates transparency with data available under the CC-BY 4.0 International license.Why GRANAR?
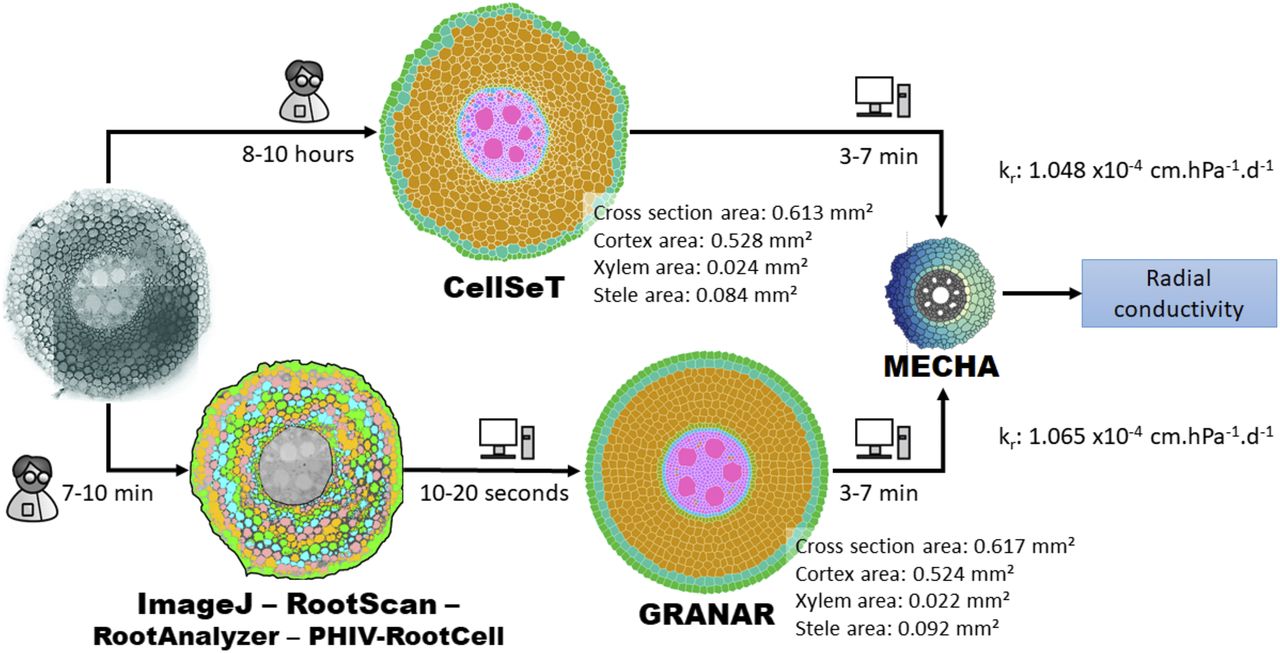
GRANAR can serve as a bridge to understanding plant roots at a cellular level, offering a detailed window into the intricate cellular networks of root cross-sections. Its capability to simulate root anatomies based on select anatomical features can make it an important tool for advanced agricultural research and plant breeding practises. Ref: the above image is taken from the GRANAR publication
- 🌾 Detailed Root Anatomy: Generates cell networks of root cross-sections from key anatomical features.
- 🌍 High Accuracy: Reproduces root cross-section anatomies with impressive precision when compared to experimental data.
- 🌦️ Versatility: Can simulate different vascular patterns, including monocot and dicot root structures.
- 💧 Integration Potential: Seamlessly integrates with hydraulic models like MECHA, providing a comprehensive view of root hydraulic properties.
- 🚜 Time Efficiency: Dramatically reduces the time required for root anatomy simulations. While other methods can take up to 10 hours, GRANAR accomplishes the task in just 10 minutes.
Dive Deeper with GRANAR

For those keen on exploring further, GRANAR offers a plethora of examples and use-cases. Discover more at GRANAR examples.