What is CPlantBox?

CPlantBox is a plant modeling framework that simulates both root and shoot system development. It represents plants as interconnected networks of organs, enabling detailed simulation of plant architectures and environmental interactions. Built on CRootBox’s foundation, it can generate diverse root architectures and implement various branching patterns. The framework integrates with photosynthesis and carbon flow modules for comprehensive plant studies.
How does it work?
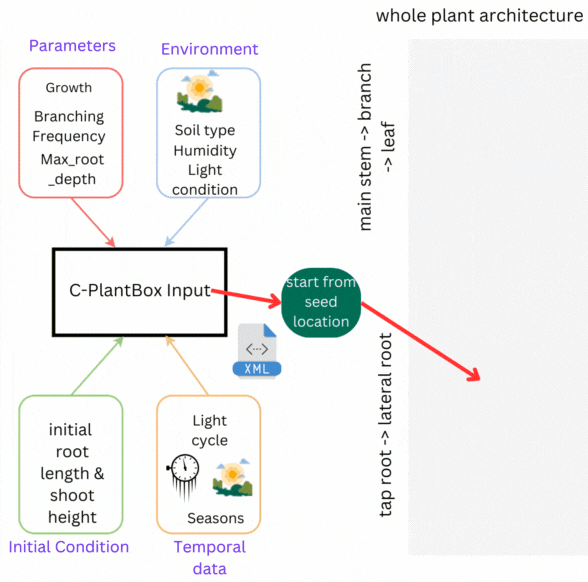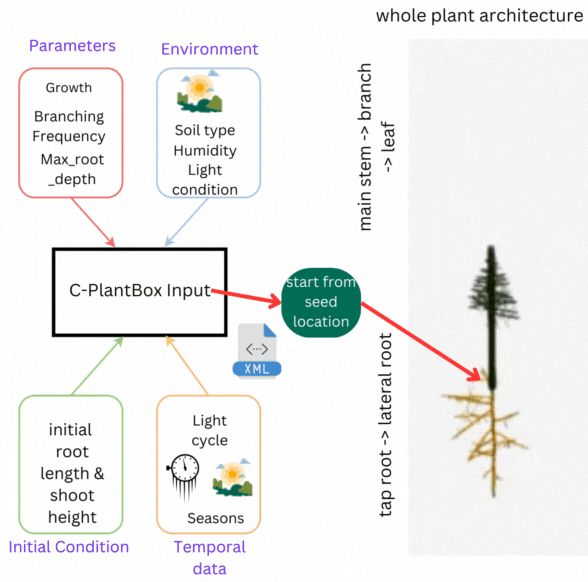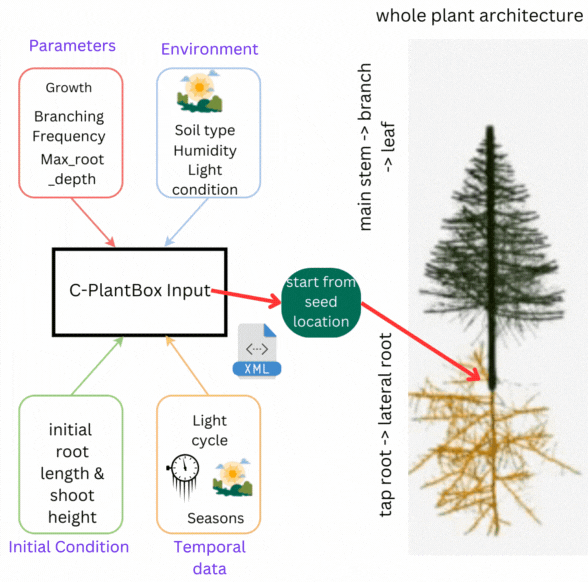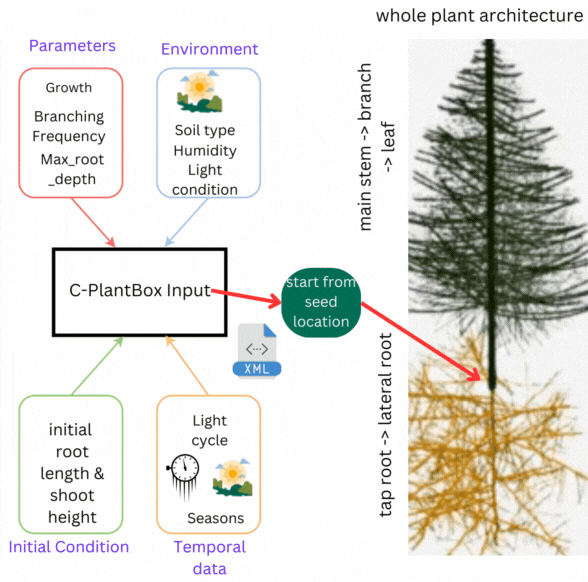
CPlantBox follows a streamlined workflow: input file generation, parameter interpretation, topological structure creation, and output visualization. The framework requires specific data structures for accurate modeling of root and shoot systems.
- 🌾 Parameter Set: Growth rates, branching patterns, and plant characteristics
- 🌍 Environmental Data: Soil conditions, humidity, light, and external factors
- 🌦️ Initial Conditions: Starting state including root length, shoot height
- 💧 Temporal Data: Time-based changes in parameters and conditions
CPlantBox features

CPlantBox integrates multiple modules covering atmospheric variables and plant water status effects on photosynthesis. It uses C++ for performance with Python’s accessibility, and connects with the PiafMunch carbon/water flow model.
- 🌾 Simulates diverse plant architectures (root and shoot)
- 🌍 Flexible coupling with external modeling tools
- 🌦️ Open source and accessible on github
| Model/Module | Purpose |
|---|---|
| PiafMunch | Handles carbon and water flow dynamics in plants. learn more |
| DuMux | Models phloem flows driven by hydrostatic pressure gradients |
| Stomatal Opening Regulation | Controls transpiration and photosynthesis based on conditions |
| Xylem Water Flow | Simulates plant water flow including lateral root/leaf fluxes |
| Mesophyll and Sieve Tube Sucrose Flow | Models sucrose transport |
| Carbon Partitioning | Simulates growth variations based on conditions |
| Photosynthesis and Stomatal Opening | Couples photosynthesis with stomatal regulation |
Tight Coupling with other models
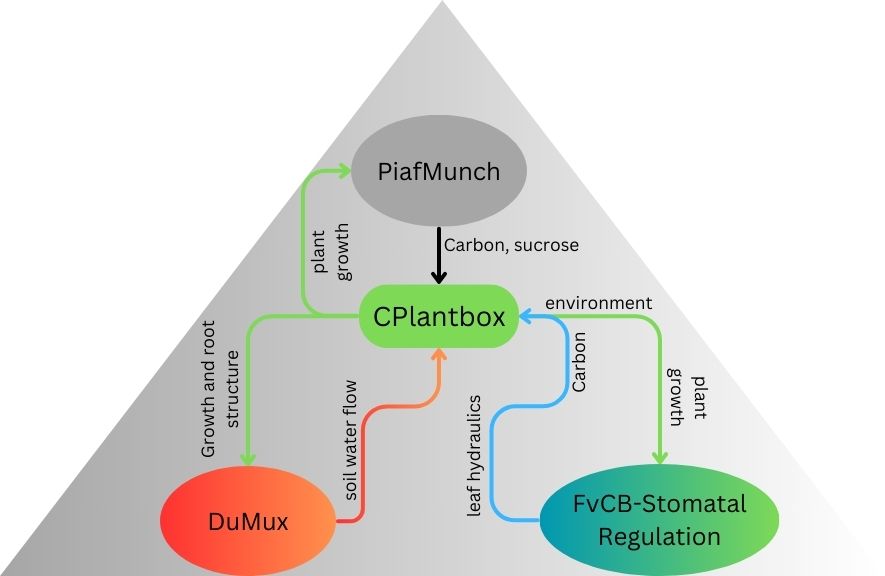
CPlantBox integrates with PiafMunch and DuMux to simulate carbon and water flow in the plant-soil system. The FvCB-stomatal regulation module enables comprehensive simulation of transpiration and photosynthesis. DuMux-ROSI represents soil-root interactions.
| Model | Parameters Exchanged |
|---|---|
| From CPlantBox to PiafMunch | Plant growth and state information affecting carbon flow |
| From PiafMunch to CPlantBox | Carbon flow and sucrose source data |
| From CPlantBox to DuMux | Plant growth and water requirement information |
| From DuMux to CPlantBox | Soil water flow and availability data |
| From CPlantBox to FvCB-Stomatal Regulation | Plant state and environmental conditions |
| From FvCB-Stomatal Regulation to CPlantBox |
|
Case Studies
Notable CPlantBox applications include:
- 🌾 Khare et al. (2022) modeling root water uptake in drying soils
- 🌍 De Bauw et al. (2020) studying phosphate uptake in upland rice root systems
Try It Online with Binder!
Experience CPlantBox through our interactive Binder environment
CPlantBox lectures
Explore plant architecture through CPlantBox modeling lectures. Learn about the mathematics and operations behind plant growth dynamics here 🌱