Cell to Organ Scale
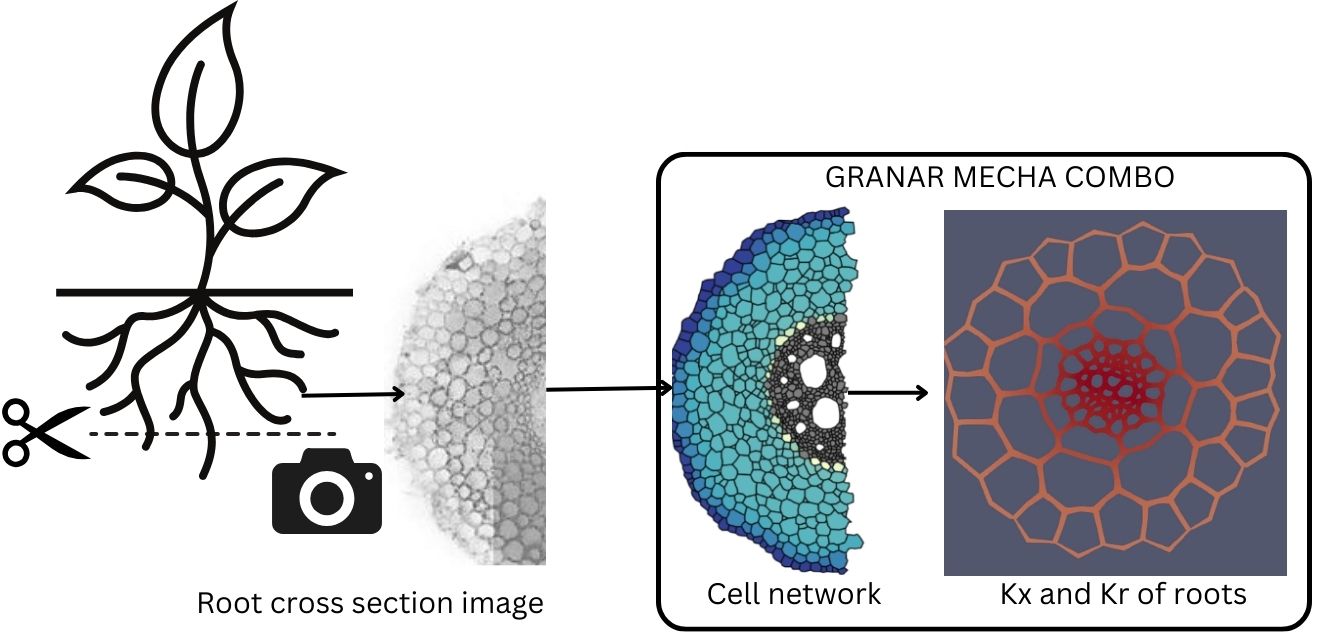
Root water uptake is influenced by structural and hydraulic properties at multiple scales. Root anatomy sets the baseline for root radial hydraulic properties. Root hydraulic properties (Kx and Kr) influences everything from crop yields to the global water cycle dynamics. While tools like MECHA allow for the analysis of water flow in roots, they require explicit anatomical networks. Obtaining these networks from cross-section images is time-consuming. Hence, there’s a need for a high-throughput method like GRANAR. The coupled GRANAR-MECHA computer model emerges as a beacon in this complex landscape. GRANAR simulates root anatomical networks. It uses key anatomical traits extracted from root cross-sections. GRANAR generates cell networks of root cross sections from a set of root anatomical features. The anatomy generation process places cell layers around the root’s center, with the position and size of each cell and layer determined by the cell type radius and user-defined randomness. Together, GRANAR and MECHA bridge the gap between the micro and macro, offering a holistic view of root hydraulic conductivity, from the behavior of individual cells to the functionality of the entire root organ.
- 🌾 GRANAR: Dive deep into root anatomy with our Generator of Root Anatomy in R. This innovative model crafts detailed root anatomical networks at the cellular level, offering a microscopic view of root structures.
- 🌍 MECHA: Introducing MECHA, our Model of Explicit Cross-section Hydraulic Anatomy. Seamlessly compute root hydraulic conductivities, both axial and radial (kx and kr), using the intricate anatomical networks crafted by GRANAR.
- 🌦️ Bridging Scales: Experience the perfect blend of micro and macro with the combined power of GRANAR and MECHA. Transition effortlessly from cellular details to organ-level dynamics, ensuring a holistic grasp of root hydraulics.
- 💧 Efficiency: Say goodbye to time-consuming processes. Harness the capabilities of our models to swiftly and accurately unravel the mysteries of the root’s hydraulic architecture.
GRANAR-MECHA Coupling
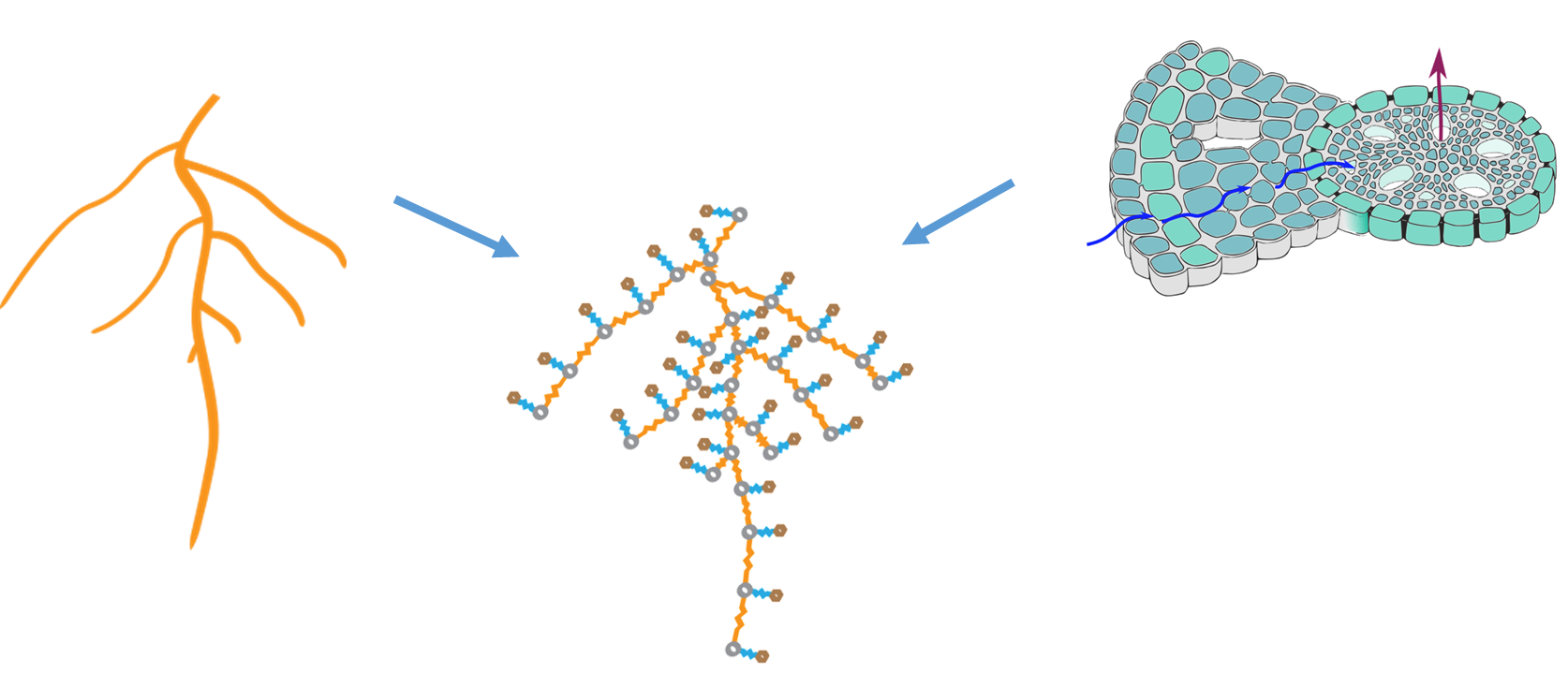
In essence, the coupling of GRANAR and MECHA allows for a systematic analysis of the impact of root anatomy on hydraulic conductivity in a high-throughput manner. This combination provides insights into how different anatomical features influence the root’s ability to conduct water.
- 🌾 Radial Conductivity (kr): The coupling study estimated the kr for each of the experimental data points.
- 🌍 Factors: The simulated kr showed variations based on several factors. These include the xylem area, total cortical area, and the proportion of aerenchyma. The most substantial correlation factor to the simulated kr was found for the cortex width
How was it Coupled ?
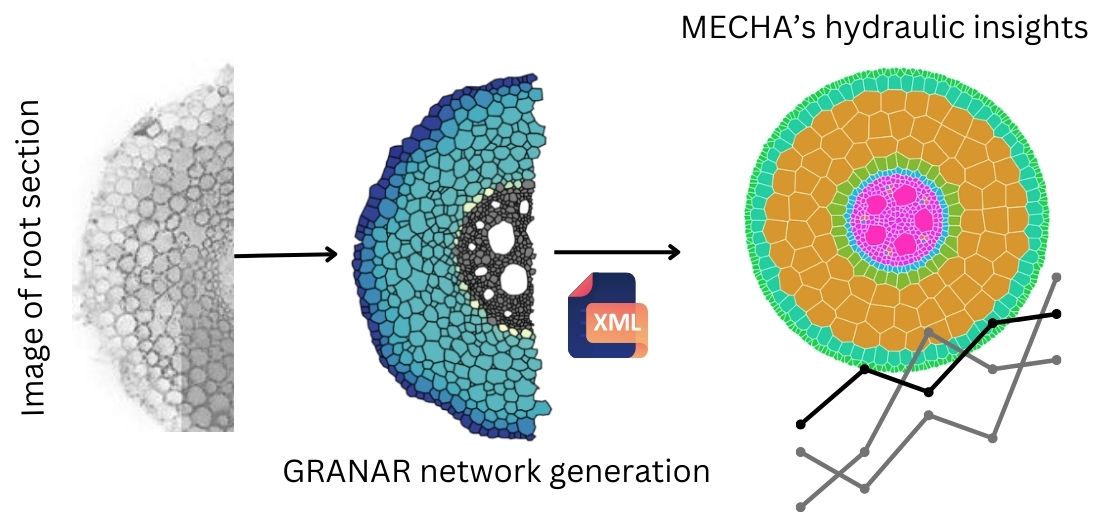
The root anatomical networks in GRANAR are crafted using easily accessible anatomical features, which can be obtained from open-access image analysis software and root cross-section images. Once the root anatomy is generated, it can be saved as an XML file. This XML file then serves as the geometry input for the MECHA model, bridging the gap between the two tools.
- 🌾 GRANAR Input: Uses tissue-scale parameters from image analysis software.
- 🌍 GRANAR Output: Produces a digital representation of root anatomy, saved in XML format.
- 🌦️ MECHA Input: Utilizes the XML file generated by GRANAR as its geometry input.
- 💧 Combined Utility: The GRANAR-MECHA model estimates hydraulic properties, such as radial conductivity (kr), for any root anatomy.
- 🚜 Software Compatibility: GRANAR outputs are compatible with other tools like CellSet, ensuring modularity.
Learn more
For those keen on exploring this coupling study further, check out the GRANAR-MECHA coupling publication