Deep Dive: Soil Compaction Insights

Soil compaction, predominantly caused by heavy machinery on agricultural land, significantly affects plant growth, especially their ability to absorb nutrients. The depth and extent of this compaction, particularly beyond 45 centimeters, remain a concern. While the damaging effects of heavy machinery like tractors and harvesters can be mitigated to some extent by tactics like reducing tire air pressure, compaction can still occur in the deeper soil strata. Techniques exist to loosen compaction up to 45 cm deep, but addressing deeper soil compaction remains a complex challenge. Delving into this issue, phenorob team conducted an innovative study. By coupling a 1D field-scale crop-soil model from the SIMPLACE framework with the 3D architectural root model CPlantbox, the team aimed to understand root behaviors and responses in compacted soil. These models operate on a daily timestep, offering insights into the nuanced interactions between plant roots and their environment.
- 🌾 Soil compaction hinders nutrient absorption in plants.
- 🌍 Deep soil compaction’s impacts on plant growth are still ambiguous.
- 🌦️ Coupled Models shed light on root behaviors in compacted soil, especially deep-rooted reactions.
Rooted Insights: Bridging Models

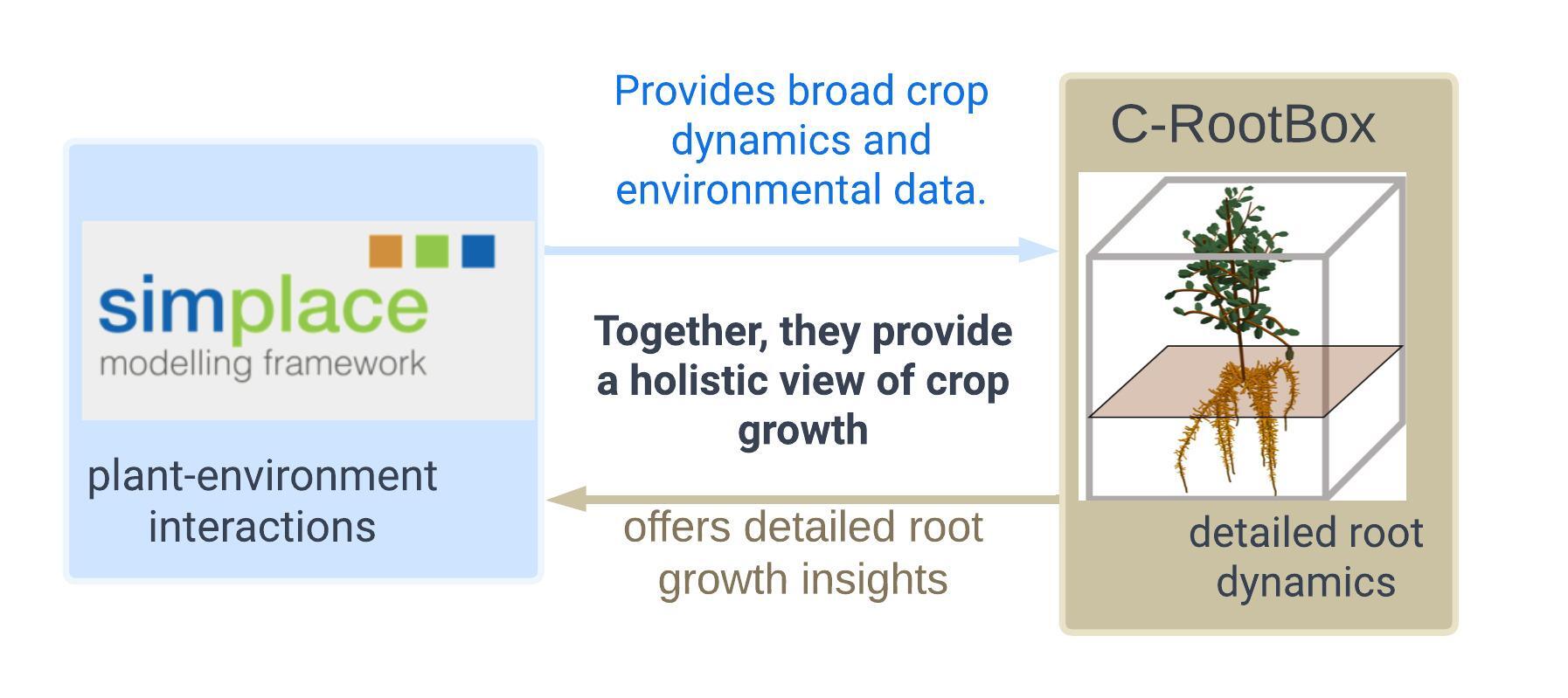
The study showcases the interconnected dynamics of soil strength and root elongation, highlighting the necessity of a coupled model to understand deep soil compaction. While the process-based dynamic model SIMPLACE offers a broad perspective on plant-environment interactions, it might not delve deep enough into root dynamics, a niche CPlantbox fills expertly. However, solely depending on CPlantbox could miss the bigger picture of holistic plant dynamics and broader field conditions. Marrying these models provides a holistic lens, capturing the complex interplay between a plant and its multifaceted environment.
- 🌾 SIMPLACE offers broad views but might miss detailed root dynamics.
- 🌍 CRootbox provides deep insights into root behaviors but might overlook larger plant-environment interactions.
- 🌦️ Coupling both models yields a comprehensive tool, enhancing our understanding of plant responses to environmental shifts.
Coupling of C-RootBox with Simplace
The dynamic coupling of CRootbox with SIMPLACE, facilitated through a Python binding, results in the SIMPLACE-cRootbox system. Within SIMPLACE, specific SimComponents such as EvapTranDemand, SlimWater, LintulPhenology, and LintulBiomass play pivotal roles in determining various aspects of crop growth and development. The daily root biomass increment calculated by SIMPLACE is transformed into a potential root elongation (RE) value, which is then provided as input to CRootbox. This potential RE is a measure of how much the roots could potentially grow based on conditions like soil quality, water availability, and nutrient levels. CRootbox then simulates the actual root system and determines the root length density (RLD). This actual RLD is then fed back into SIMPLACE. If the potential RE from SIMPLACE exceeds the maximum possible elongation, CRootbox proportionally reduces root growth. This creates a feedback loop where the root biomass provided by SIMPLACE determines the maximal root elongation, ensuring that root growth limitations due to soil physical stresses are considered before potential root growth limitations due to biomass provided by the shoot.
- 🌾 Integration:CRootbox and SIMPLACE are coupled to provide a realistic representation of root growth
- 🌾 Method: Python interface between the two models.
- 🌍 Result: Combined system termed SIMPLACE-cRootbox.
- 🌍 SIMPLACE Components: Specific components like EvapTranDemand, SlimWater, LintulPhenology, and LintulBiomass are involved in the process
- 🌾 EvapTranDemand: Estimates potential crop transpiration and potential soil evaporation using a modified Penman approach.
- 🌍 SlimWater: Computes soil water dynamics, estimating daily change in soil water content based on factors like crop water uptake, soil evaporation, surface runoff, and seepage below the root zone.
- 🌦️ LintulPhenology: Calculates the development stage of a crop.
- 💧 LintulBiomass: Determines daily root biomass increment.
- 🌦️ Data Flow
- 🌾 From SIMPLACE to CRootbox: Potential root elongation (RE) derived from SIMPLACE’s components.
- 🌍 From CRootbox to SIMPLACE: Actual root length density (RLD) simulated by CRootbox.
- 💧 Feedback Mechanism:Ensures that root growth limitations due to soil physical stresses are considered before those due to biomass
- 🌾 Growth Prioritization: Emphasis on soil factors over shoot-derived biomass restrictions.
- 🌍 Mathematical Representation: If \( RE_{potential} > RE_{max} \), CRootbox adjusts to ensure \( RLD_{actual} \leq RLD_{potential} \). In other words, if potential root elongation was higher than the maximum allowed, CRootbox would reduce root growth equally across all roots
Impact of Soil Loosening on Crops
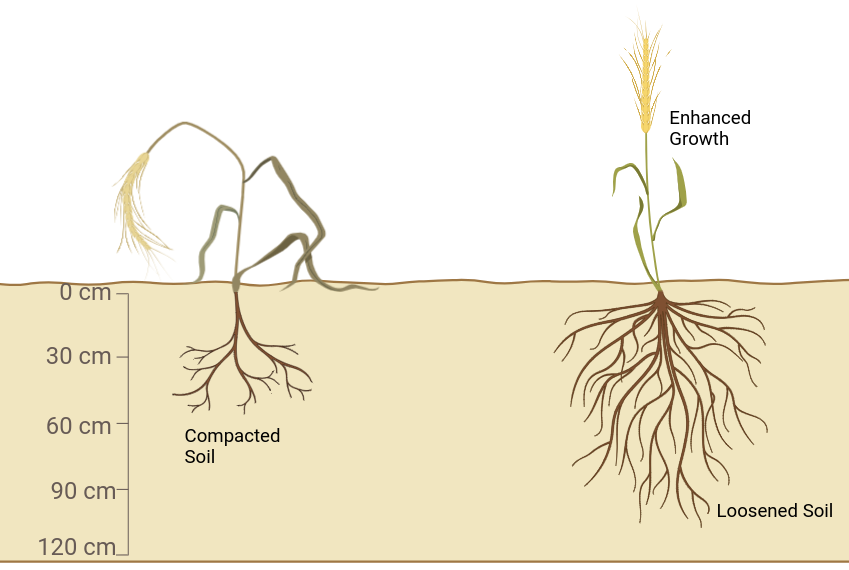
The study used the integrated SIMPLACE-CRootbox model to explore how deep soil loosening affects the growth of spring barley and winter wheat. The model highlighted the relationship between soil compaction, weather, and crop species, emphasizing the role of soil strength. Here are the key takeaways:
- 🌾 Enhanced Growth with Loosening: Deep loosening improved root growth, leading to better crop productivity, especially in dry conditions.
- 🌍 Model Accuracy: The model effectively simulated root growth from emergence to flowering, capturing the effects of subsoil loosening on both roots and shoots.
- 🌦️ Soil Compaction Insights: Soil strength, influenced by compaction and moisture, plays a crucial role in root growth. Dense layers can restrict access to deeper soil moisture, especially in warmer climates.
- 💧 Agronomic Implications: Understanding root adaptation to soil conditions can guide cultivar selection and breeding, promoting sustainable agriculture.
- 🚜 Model’s Potential: This tool can assess the impact of different root traits under various conditions, paving the way for advanced cultivar research and selection.
Implications of the Study
The integration of SIMPLACE and CRootbox models provides insights into root-soil interactions and soil compaction effects. This coupled model simulates relationships between soil compaction, weather, and crop species, offering information relevant to agricultural productivity under varying environmental conditions. The model’s simulation of root adaptive plasticity to local soil conditions allows for the exploration of genotype-environment-management interactions. This capability may assist in cultivar selection and research on root traits. The model’s approach to analyzing root growth patterns and their impact on yield could contribute to the development of agricultural practices.
- 🌾 Root-Soil Interaction Analysis: The coupled model examines root-soil interactions, including soil compaction effects.
- 🌍 Root Adaptability Simulation: The model simulates root adaptive plasticity to local soil conditions, which may inform cultivar selection and breeding research.
- 🌦️ Crop Ideotype Exploration: The model can be used to investigate potential future crop ideotypes for specific environmental conditions.
- 💧 Genotype-Environment Interactions: The model allows for the study of genotype-environment-management interactions, potentially informing breeding research.
- 🚜 Agricultural Practice Insights: By analyzing soil compaction and weather effects on crop species, the model may contribute to agricultural practice development.
- 🌾 For further details on this study, refer to the article published in Frontiers in Plant Science
Installation Guide: SIMPLACE-CPlantBox
This section provides the installation guide for setting up SIMPLACE-CPlantBox, along with insights into the Python script that controls the coupling between the models.
- 🌾 Prerequisites
- 🌾 Create a folder ‘workspace’ in your home directory.
- 🌍 Make sure the required modules are loaded in your system.
- 🌍 Repository Checkout
- 🌾 Checkout the simplace_wrapper from the SVN repository
svn co svn://svn.simplace.net/svn/simplace_wrapper simplace_wrapper. - 🌍 Navigate to example folder and give execution rights to installation shell scripts. For e.g
chmod +x SIMPLACE_v5.0_install_bonnares.sh
- 🌾 Checkout the simplace_wrapper from the SVN repository
- 🌦️ Installation Steps
- 🌾 Execute the shell scripts to download and compile SIMPLACE and CPlantBox.
- 💧 Python Script Configuration
- 🌾 Python script accepts command-line arguments for various parameters like solution ID, rain scale, and crop type.
- 🌍 Script initializes root system and sets up simulation parameters.
- 🚜 Running an Example
- 🌾 Load the required modules.
- 🌍 Run the example script located in misc/example_simplace_cplantbox.py.
- 🌦️ Python script controls the iterative interaction between SIMPLACE and CPlantBox, updating parameters and fetching results at each simulation step.