What is AgroC?
AgroC is a 1D model integrating the SOILCO2/RothC and SUCROS models, designed for advanced simulation of carbon fluxes, soil processes, and crop growth. It excels in complex analyses such as CO2 and heat flux simulation in soil, root respiration, and autotrophic/heterotrophic interactions in agricultural ecosystems. AgroC employs rigorous methods like the one-dimensional profiles of soil water and temperature for carbon turnover rate calculations, showcasing its high precision in ecosystem modeling.
Components of AgroC Model
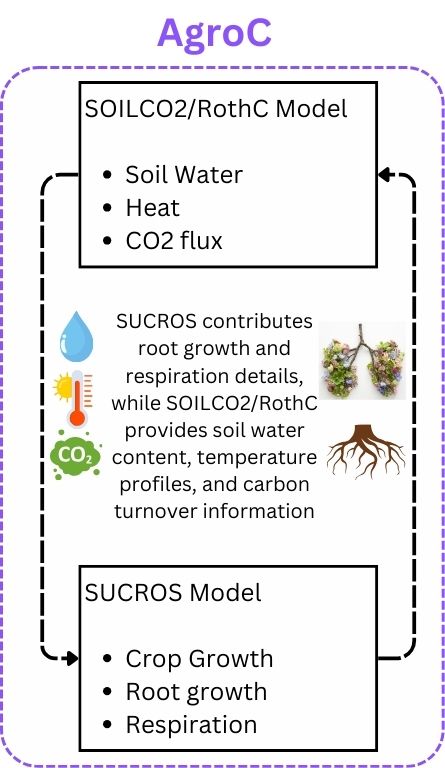
The AgroC model encompasses several specialized components, each addressing different aspects of agricultural simulation. The SUCROS model focuses on crop growth, calculating photosynthesis and biomass accumulation, employing the Farquhar model for accuracy. The SOILCO2 module simulates soil processes, including water and CO2 fluxes, and uses Richard’s equation for soil moisture balance. RothC integrates with these to simulate soil carbon turnover, evaluating factors like Gross Primary Production and ecosystem respiration, and achieving a comprehensive carbon balance. Here is the documentation for AgroC
Software and Implementation
AgroC is developed using Fortran90, a powerful and widely-used programming language for numerical and scientific computing.
- 🌾 Compiler Requirement: To install and run AgroC, you will need a Fortran compiler.
- 🌍 Platform Support: The model comes with a makefile for Linux and Mac. However, for Windows users, the installation and setup process is more manual and might require additional steps.
- 🌦️ Code Repository: The source codes for AgroC can be accessed and downloaded from the SVN repository. Use the following command to checkout the latest version:
svn co svn://icg4lts.icg.kfa-juelich.de/agroc_codes_v3.
Case Studies
AgroC has been instrumental in advancing our understanding of crop growth dynamics, soil interactions, and effective agricultural management strategies. The following case studies illustrate AgroC’s capability to adapt to different regional climates, management practices, and specific agricultural needs, providing invaluable insights for future agricultural planning and sustainability.
- 🌾 Brogi et al. 2020 showcased AgroC’s application in simulating crop growth and yield relative to soil properties over a square kilometer scale. By integrating a geophysics-based soil map with land use information, the AgroC effectively simulated soil water content dynamics and crop growth for a variety of crops such as sugar beet, maize, potato, wheat, barley, and rapeseed. The study highlights AgroC’s accuracy in replicating observed leaf area index and yield data, underscoring its potential in precision agriculture and strategic decision-making.
- 🌍 Constantin et al. 2019 illustrated AgroC’s role in a comparative study assessing the impact of crop management and spatial data resolution on regional-scale crop model outputs. In this research, AgroC, among other models, was used to simulate winter wheat and maize over 30 years in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The study explored adaptive management strategies considering local climatic conditions, such as varying sowing dates and nitrogen fertilization, and assessed their effects on crop yield, evapotranspiration, and drainage. Notably, AgroC’s predictions showed particular sensitivity to these management changes, underlining its utility in modeling agricultural systems where management practices and spatial resolution are crucial factors.
- 🌦️ Groh et al. 2020 demonstrated AgroC’s effectiveness in a model intercomparison study on crop growth and soil water fluxes at erosion-affected sites. Utilizing the TERENO-SOILCan lysimeter network, AgroC effectively simulated various agronomic and environmental variables, emphasizing its critical role in modeling and understanding the complexities of agricultural systems influenced by soil heterogeneity.
- 💧 Maharjan et al. investigated how using different levels of detailed information (data aggregation) affects predictions of crop yields in Mediterranean and temperate climates using AgroC and other models. The study revealed significant differences in data aggregation effects between these climates, particularly for spring crops in the Mediterranean region. This highlights the importance of using detailed local data for reliable crop forecasts, especially in areas with diverse weather and soil conditions.
- 🚜 Žydelis et al. examined how cooler weather and limited water supply affect maize growth, using the AgroC model. The study, conducted in a region with a cooler climate, showed that AgroC can accurately simulate maize growth in these challenging conditions. It was found that cooler weather has a bigger impact on maize yields than occasional water shortages. This research is important for understanding how to grow maize in areas with cooler temperatures, highlighting the usefulness of AgroC in adapting farming practices to different environmental conditions.
AgroC Videos
The videos here demonstrate how AgroC can flexibly accommodate diverse regional climates, management approaches, and specific agricultural requirements: